Logging into an account only to find that the password no longer works can be an alarming experience. This likely indicates that the password has been compromised. Cybercriminals use various methods to guess passwords, ranging from straightforward to extremely sophisticated. The increase in computing power means that the time required to crack a password has significantly reduced over recent years. Understanding how long it takes to crack your password is essential for maintaining a secure online presence. Complex and lengthy passwords are your best defense against these attacks.
A study by Hive Systems reveals that advancements in computing have drastically reduced password-cracking times. For instance, a seven-character password made up of numbers can be cracked in as little as four seconds, whereas a 9-character password with a mix of upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols could take about 479 years to break. These findings highlight the necessity for longer, multifaceted passwords.
What is password cracking?
Password cracking involves cybercriminals using various tools and techniques to recover passwords from stored data. These methods range from systematic guessing to complex algorithms that expedite the process, all with the aim of gaining unauthorized access to systems, networks, or accounts. Once hackers uncover a user’s password, they can steal sensitive data or disrupt operations.
Techniques for cracking passwords vary in their complexity and success rates. For example, a brute force attack tries every possible combination of characters until the correct one is found, making it effective against weak passwords but time-consuming. On the other hand, social engineering involves manipulating individuals into disclosing confidential information.
The repercussions of password cracking are extensive. Once hackers gain access to your password, they can carry out unauthorized financial transactions, steal data, and commit identity fraud. To prevent such invasions, users need to understand these techniques and take proactive steps to safeguard their online credentials.
How long it would take to crack your password
Password strength holds our security together in our digitized world. The length, characters, and complexity of a password are some of the factors that determine the time to crack your password. Check out this password length cracking chart:
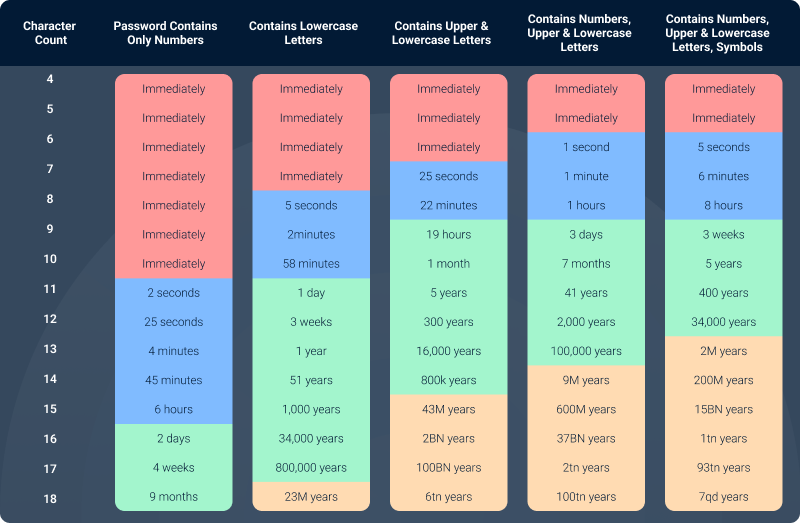
Below is the breakdown of how those factors affect the time it takes to break a password:
Password characteristic
- Contains only numbers
- Contains lowercase letters
- Contains numbers, upper & lowercase letters
- Contains numbers, upper & lowercase letters, symbols
Password length
- Short passwords (1-4 characters): These can be cracked immediately regardless of their complexity.
- Medium-length passwords (5-8 characters): Greatly adding to the complexity really adds to the time it takes to crack. A 7-character password with upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols all take approximately 5 hours to crack, whereas if it is all lower case letters, that drops to 22 minutes.
- Long passwords (9-12 characters): All these will go, in a very good way, to help defend against cracking, more so if they are a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. A 10-character password including all these would take approximately 45 million years to crack.
- Very long passwords: These come very close to being unbreakable and especially when they are complex. A 13-character password with a mix of characters and symbols can reach up to 100 trillion years for cracking.
The length and complexity of the password are important when securing your account from hacking. It’s always very advisable to have a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, symbols, and at least 12 characters for maximum safety.
Factors that impact the ability to crack your password
The following factors will reduce or stretch out the time it takes for someone to guess your password, making it easier or harder to do so:
- Length: The shorter the password, the easier it is to crack; the more characters, the safer.
- Character variety: The use of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols increases the complexity.
- Common patterns: Avoid using sequences, repeated characters, and very common passwords.
- Dictionary words: Using common words, with substitutions, still makes them vulnerable to dictionary attacks.
Modern password-cracking tools can, therefore, exploit these vulnerabilities. For instance, dictionary attacks involve using lists of common passwords and variations in an assault on a password at quickened speeds. Such attacks are very susceptible to passwords that lack complexity, like sequences or repetitions.
A password should be personalized by avoiding easily-guessable information. That includes birth dates, anniversaries, or other straightforward phrases. Such passwords are least predictable and unlikely to get attacked by hackers.
This will go along in significantly reducing the risk of a breach. Changing your passwords at intervals and not using the same password for multiple accounts will go a long way in keeping off hackers. Two-factor authentication makes it even harder for intruders to get into your account.
Password cracking methods
Brute force attack
In a brute force attack, all possible permutations of characters are tried until the right password is found. This is time-consuming but has absolute success against weak passwords. Most contemporary systems have implemented mechanisms to prevent basic brute force attacks; however, sophisticated variations of the attack still cause a problem. With the processing power of today’s hardware, it can be done very quickly, and the time taken to crack simpler passwords becomes much less.
Rainbow table attack
Rainbow tables are precomputed tables of hashed values matched to plain-text passwords. Hackers will often reverse-calculate passwords quickly from hashed information using these kinds of tables. This form of attack is thus rated efficient for password cracking. The bottom line in their efficiency comes from the idea that hash values are pre-computed from the probable password patterns in advance, which a hacker could possibly bypass while applying hashing algorithms. However, the use of salt—random data added to the passwords prior to hashing—can make rainbow tables futile.
Social engineering
In social engineering, information is obtained from people by deceiving them, normally through psychological manipulation. Rather than technical, it exploits the human element in behavior. Phishing emails and fraudulent calls become very common in social engineering. In fact, even pretexting—building a situation to create trust—is used by hackers before they can actually extract sensitive data from targets. First-line defenses against this include policies, training, and awareness among the users.
Phishing
Phishing emails fool users into giving away their passwords by sending emails or messages that appear to be from a trusted institution, sometimes redirecting them to a fake website. This is a very effective technique and is usually combined with other attack vectors. From very basic techniques like spear phishing—focused on individual targets—to whaling—the targeting of highly important individuals—phishing continues to evolve. Awareness of the telltale signs of such emails and checking sources decrease the chances of being phished.
Keystroke logging
Keyloggers record everything one types on a computer, including passwords. Hackers launch the process by installing keyloggers, either through malware or by gaining direct access to the device; therefore, it is quite effective in harvesting confidential information. Most often, keylogging malware functions in the background, unnoticed, logging data for weeks or even months. Ensuring that anti-malware software is installed and updating system security patches can prevent keyloggers from invading your computer.
Malware
Malware is when the software is developed to infiltrate, cause damage to systems, and do other sorts of desired harm. Some of these malware types are aimed at retrieving previously saved passwords or allowing remote access, hence capturing sensitive information from users’ devices. Given its ability to spread from device to device, this could actually escalate into a bigger scale of breach once malware has penetrated a system. Updating operating systems and applications, along with reputable security solutions, immensely reduces the possibility of malware infections.
Man-in-the-middle attack
In man-in-the-middle attacks, hackers hijack a communication line of two entities to steal data, which, of course, includes passwords. This is quite dangerous, especially when working on unsecured or public networks. This then calls for ensuring a safe connection while transmitting data, as technologies like HTTPS and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) ensure that data is safe from interceptions. Ensuring sensitive activities, such as banking and online shopping, are done on secured connections cements a strong defense.
Improve password security
There are a few things you can do to enhance your password’s security. Here are some of them:
1. Monitor your passwords for breaches with WOT
WOT provides real-time password monitoring. Upon switching “Information Leak Alerts” on under the Data Privacy feature, this tool will find password leaks and will help in keeping your data private and letting you know in the case of exposure or being tracked for sensitive information. This service will keep you ahead and allow you to take necessary actions promptly if your passwords are compromised.
WOT keeps scanning public databases for any occurrence of your password being compromised and lets you know this immediately to act upon it. In this way, proactive monitoring keeps users ahead of potential threats by acting before the onset of harm.
2. Make passwords longer and more complex
For a secure password, aim for at least 16 characters, mixing uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. The longer and more complex, the considerable times they are much harder to crack.
Definitely avoid easily guessable details such as:
- Birth dates
- Pet names
- Common phrases
Complex passwords are unique for each account, and thus, in case one is compromised or exposed, the others won’t be affected.
3. 2-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds another layer of security by requesting one more form of verification, like a code that will be sent to your mobile device. This approach significantly reduces the probability of unauthorized access to data even if your password is compromised.
A strong 2FA will make use of biometrics, hardware tokens, or time-based one-time passwords. Enabling 2FA on all accounts and especially sensitive ones dramatically improves your security posture.
4. Use a password manager
They generate and securely store complex passwords. This means you can have unique passwords for all your accounts, without having to remember each one.
Password managers can autofill credentials on trusted sites, so you use strong varied passwords consistently—with no mental effort. Using a reputable manager ensures your data is stored securely and conveniently accessible.
A safe tomorrow begins today
Securing all your online accounts should begin with secure passwords. Keeping an eye out for breaches, having longer and more complex passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and employing a password manager really bring the possibility of your passwords being cracked down to near zero. And of course, utilize tools such as WOT to stay a step ahead of the cybercriminals and be safe.
Don’t let it be too late. Save your passwords today by taking control of your online security. Explore other powerful features of WOT to get more enhanced password protection against cyber threats. Secure your passwords and help ensure a safer experience on the web.
FAQs
How do I create a strong password?
A strong password must be at least 16 characters long. It may consist of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols. Avoid the use of common words, sequences, and personal information to secure your password.
What are some indications of a phishing attack?
Here are some of the common signs of phishing emails: unsolicited mail seeking sensitive information, general greetings, grammatical errors, and links that raise suspicion. Always check the authenticity before submitting any confidential information.
How often should I change my passwords?
Change your password every three to six months, or whenever you feel one of your accounts has been compromised. Use a password manager for frequent changing of passwords with no sweat.
Is it OK to write down my passwords?
It is very dangerous to write down your password since all one has to do is find your notes and he will get access. To the contrary, a password Manager can generate, store and retrieve complex passwords securely.
What if I think my password has been compromised?
If you think that someone might have learned your password, change it now. Also, turn on two-factor authentication for safety and see if there’s any unwanted activity. Let your service provider know about this breach, too.
