Many people have a big issue with their privacy on the internet. As you browse, leaving digital fingerprints behind you, third parties might follow you, watch you, and keep track of your actions. Incognito mode, found in all popular browsers, offers better privacy by not saving your browsing history, cookies and site data on your local device. It might also clear information stored by previous versions of the browser (if any). Even if incognito mode is used by a great number of internet users, there are plenty of misconceptions about the level of privacy it provides. There are also a couple of features, which people seem to misunderstand.
In the age of hackers, data breaches, and other digital threats, many people are becoming more concerned about their privacy online. Incognito mode is an option that can help users ensure that their browsing activity is kept private, especially when searching on a shared computer in a public place. Despite its benefits, it’s important for users to understand the limits of how much privacy incognito mode can actually provide them with. Many users often remain confused about what incognito mode is capable of. This guide will detail what incognito mode is and how it functions, with information about how much privacy it truly offers.
What is incognito mode?
Incognito mode, also known as private or stealth mode, is a feature of many web browsers that removes the ability to store browsing history, cookies, site data, and form information from your local device. In this mode, information such as what pages you have visited or the information you have entered into forms is not saved by your browser. This mode is commonly used in a shared or public space where you do not want the pages you visit to be viewed by those coming after you. There is an incognito mode available in every major browser:
- Google Chrome: Incognito Mode
- Microsoft Edge: InPrivate Mode
- Mozilla Firefox: Private Browsing
- Apple Safari: Private Browsing
What does incognito mode do
When you activate incognito mode, various local privacy protections are enacted. Here’s what happens:
- Prevents your browser from saving your browsing history.
- Stops cookies and site data from being stored after your session ends.
- Starts a new session with every incognito window, discarding all session data when closed.
Your browser treats you as an anonymous user on every site you haven’t created an account on before. This can be great when you want to make online shopping or research purchases without ads tailoring the results based on your browsing history. Since there are no cookies or cache, you won’t be automatically logged into any accounts you previously visited. This is great for testing environments, fixing issues, or for living a low-key lifestyle online for a day.
It is important to note, though, that incognito mode is not a cure for all ills. Sure, you can keep most of the information on your local machine to yourself, but incognito does little to prevent the collection of your broader internet activities. Websites are still able to use your IP address to nail you down – and, once you log into an account, that service knows everything you are doing. Your school, your boss, and your ISP can still see everything you do online.
Does incognito work?
The degree to which incognito mode works depends on what you’re trying to achieve, but when it comes to not wanting your browser to store history and cookies, it’s effective. Knowing that one’s browsing history can’t be stored on the computer locally is valuable for anyone using a shared or public machine and who cares about not leaving a trace of their activity for someone else to stumble upon.
While this mode will stop sites from storing data on your computer, it won’t make you invisible to websites, ISPs, or network administrators, since sites can still track you based on your IP address and other means such as digital fingerprints. For this reason, if you want to be absolutely anonymous, you need other tools as well.
Although incognito mode keeps your browsing history private from other users of your device, on its own it is not sufficient for users who want more robust privacy protections. Things you do online that you want to keep private – like sensitive research or communications – need more than just incognito mode. That’s why understanding its benefits and limitations helps you make better choices about protecting your online privacy.
Benefits of incognito mode
Incognito mode is an amazing tool that has many advantages which makes it helpful for everyday activities on the internet. Below are some of its advantages:
Privacy on shared devices
In incognito mode, your browser history activities are invisible to any other user of the device, and you can check your email or research whatever you like without anyone knowing.
Temporary sessions
You can use it to access any account temporarily — you could read a work email on a stranger’s computer without leaving any traces.
Reduced personalization
Without cookies from previous visits that advertisers’ websites and ad services can use, targeting ads becomes much less precise. Your browser might become less biased.
Debugging and testing
Sometimes, web developers use the incognito mode to check how their site loads and looks, and how it works without cache or cookies. It’s as if they are testing what the site will be like if the visitors access it, or as if they are simulating the experience as the visitors themselves.
Limits of incognito mode
Although incognito mode has several advantages, it also has several drawbacks that users must be aware of:
Limited anonymity
Perhaps one of the biggest drawbacks of using incognito mode is that it’s only partially anonymous. While it inhibits your local storage of browsing data, it doesn’t obscure your activities from any group outside of your computer – namely websites, ISPs, and network admins. These groups can track what websites you’re going on and what activities you’re performing every step of the way. Incognito mode, as a result, is no magic wand to online anonymity. Your IP address is still visible, and your activities can still be tracked via other methods.
No security against malware
Another limitation is that incognito mode does not guard against malware or phishing attacks at all; it is not a defense against these threats. Only dedicated security software can be used to avoid these dangers, and going incognito alone can create a false sense of security about this issue. Users might not take the time to install dedicated security software and instead think that incognito mode will keep them safe. This is clearly not the case. To avoid this, regular antivirus updates and perform malware scans, and ideally use a dedicated tool to detect phishing websites.
Persistent logged-in states
Incognito mode prevents the local storage of browsing data, but websites you visit can still track you once you’re logged in to your accounts. Your activities are still recorded, and you’ve unintentionally defeated the purpose of incognito mode. If you need true privacy for sensitive online activities, remember to combine incognito mode with other tools like VPNs (virtual private networks) and a good antivirus program.
How to use incognito mode
It’s easy to turn incognito mode on: just follow a few steps, depending on your browser: How to use it across major browsers:
Chrome
Desktop
Fire up Chrome then hit Ctrl + Shift + N (Windows) or ⌘ + Shift + N (Mac). However, you can also do it manually by clicking those three vertical dots next to your profile badge and selecting New Incognito Window.
Mobile
Tap the square with a number in the bottom navigation bar on the Chrome app, then click the hat and glasses icon to open an incognito window.
Safari
Desktop
On Safari, open a new private window by pressing the shortcut key ⌘ + Shift + N (Mac) or through File and New Private Window.
Mobile
Tap the dots in the bottom-right corner of the Safari app window, then tap the two overlapping squares in the top left to open Tab Overview, then tap the icon with three lines and dots at the bottom left, then tap Private under Tab Groups.
Edge
Desktop
Open Edge, and use the shortcut Ctrl + Shift + N on your keyboard (Windows) or ⌘ + Shift + N on a Mac, or choose ‘New InPrivate Window’ from the menu (the three horizontal dots).
Mobile
Open Edge, hit the three dots at the bottom and choose ‘New InPrivate tab’.
Firefox
Desktop
Open Firefox and press Ctrl + Shift + P (Windows) or ⌘ + Shift + P (Mac) or go to File, then New Private Window.
Mobile
Launch Firefox, tap the little rectangle with a number in it, and then the mask icon to open an incognito window.
Should you use incognito?
Whether or not you should browse in incognito mode depends on whether you care about your privacy. Using incognito will keep others, such as people who might use your computer after you’ve left, from seeing what you’ve searched for, or what cookies and site data you’ve accumulated. It’s the digital equivalent of using a public library computer.
Incognito mode will protect you from other users and network administrators, but for high-level privacy that keeps your activities hidden from ISPs, look into other tools such as VPNs which encrypt your data and obscure your IP address. For most people, incognito mode offers useful solutions to everyday browsing problems; it is not a serious privacy tool.However, using incognito mode does not make you safe from malicious links or websites. Even if you are in this private browsing mode and you click on a suspicious link, your computer may end up getting infected. To make it even more difficult for such attacks to take place, you can use WOT’s Safe Browsing feature while you are incognito.
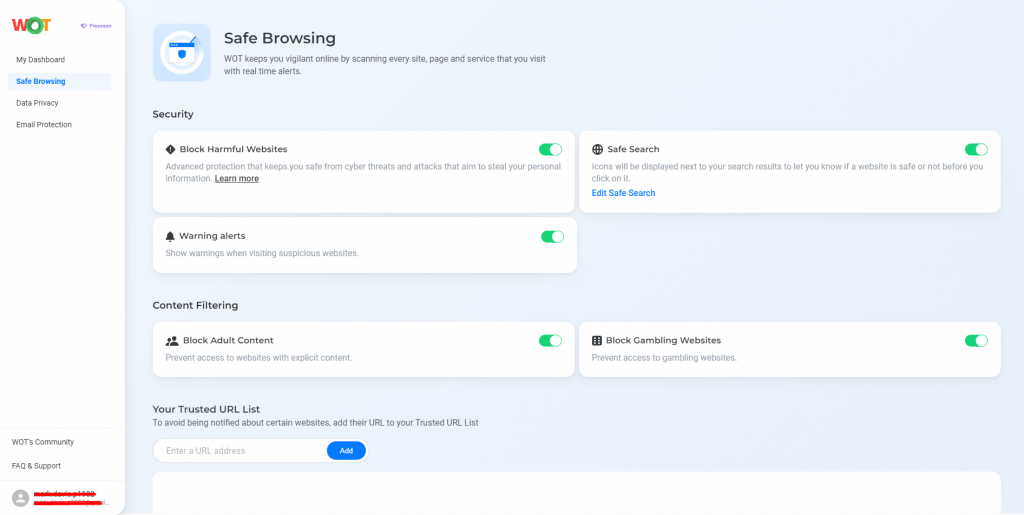
This way, if WOT spots a harmful or suspicious site, you’ll be warned and you will stay safe, regardless of browsing mode.
Your next steps for online privacy
Incognito mode is a great way to stay private while browsing locally, and it’s useful for shared devices, to avoid cookie-based ad targeting. But it’s not a replacement for dedicated privacy tools such as VPNs, which offer more robust privacy. Always consider the specifics of your situation and complement incognito mode with other privacy tools to make your experience safer. Integrate extra privacy to your browser and enjoy an extra layer of security when going online.
FAQ
What is the difference between incognito mode and a VPN?
Incognito mode is just hiding the browsing history and cookies on your PC. A VPN encodes your internet traffic so no one between you and the server can see it, and hides your IP address so it can’t be traced. This is why a VPN offers much more online privacy and security than incognito mode.
Can I be tracked in incognito mode?
Yes, the sites you visit and (most) ISPs and network administrators can still track your activity, since Incognito mode merely blocks local storage on whatever device you’re using. It can’t hide your IP address, nor the data you send across the internet.
Does incognito mode block ads?
Not necessarily. Because incognito mode prevents the storing of cookies, it reduces the ability of advertisers to serve you personalized ads based on what you’ve recently viewed. But it won’t stop every ad, as many are delivered based on what a site is about rather than your own browsing behavior.
Can I use extensions in incognito mode?
Yes, in most browsers you can enable specific extensions only in incognito mode, although you have to turn them on in your browser options of each extension or plugin to make sure that they don’t save or send your data outside incognito sessions).
Is using incognito mode on public Wi-Fi safe?
Incognito mode is a privacy feature on public Wi-Fi that prevents your browsing history from being saved. It’s not a complete security solution, though it can help protect against so-called man-in-the-middle attacks and insecure sites. A VPN is better for privacy and encryption.
