What is the Difference Between Mobile Security Vs. Computer Security
Today’s tech security concerns highlight the differences between mobile and computer protection. Mobile devices often face unique challenges, such as app-based threats and continuous online exposure, and this makes them more susceptible to attacks. They need security measures that protect apps and personal information. In contrast, computers, with more established security systems, focus on combating malware, phishing, and unauthorized access.
Both platforms demand tailored strategies to defend against specific risks and maintain user safety, with mobile security focusing more on app safety and data protection, while computer security emphasizes malware defense and access control.
Mobile Security: Risks and Threats
Mobile security faces numerous threats that can compromise personal information, financial data, and overall privacy:
Malicious Apps
One significant risk is the presence of malicious applications. These apps, often disguised as legitimate software, can infiltrate devices to steal data, monitor user activities, or hijack device functions. Unsuspecting users may inadvertently download such apps from third-party app stores or deceptive links.
Phishing
Phishing attacks on mobile are increasingly sophisticated. Cybercriminals use fake emails, SMS, and pop-ups designed to mimic trusted entities to lure users into providing sensitive information. The mobile interface, which often displays less information on screen, aids fraudsters in their efforts to deceive users about the authenticity of their communications.
Network Threats
Network threats are another major concern. Mobile devices frequently connect to public Wi-Fi networks, which may not be secure. Attackers can intercept data transmitted over these networks, such as login credentials and credit card information, through techniques like man-in-the-middle attacks. The use of unsecured Wi-Fi networks at places like cafes, airports, and hotels significantly increases the risk of such breaches.
Physical Loss
Loss or theft of mobile devices also poses a unique security challenge. Unlike stationary computers, mobile devices are carried around and can easily be lost or stolen. The physical loss of a device not only means the loss of expensive hardware. It also opens up the possibility of data theft if the device is not adequately secured with a strong lock screen, encryption, or remote wipe capabilities.
Ransomware and Spyware
Ransomware and spyware have also begun to target mobile platforms aggressively. Ransomware locks users out of their devices or encrypts files, demanding a ransom to restore access. Spyware, on the other hand, silently monitors user activities, collects sensitive data, and transmits it to third parties without the user’s knowledge or consent.
Interface Threats
Threats like these include UI redressing, where attackers manipulate the user interface to trick users into performing actions they would not intend to. This could involve overlaying a fake interface over legitimate buttons, which may lead users to click on areas that trigger malicious activities under the guise of regular interactions.
Gateway for Cyberattacks
Lastly, the integration of mobile devices with other personal and smart home devices creates a network of interconnected technology that can also serve as a gateway for cyberattacks. Once a hacker gains access to one device in this network, they can potentially access others, compromising security across a range of connected technology.
Computer Security: Risks and Threats
Computer security involves dealing with various sophisticated and harmful threats:
Malware
One major risk is malware, including viruses, worms, and Trojans. These malicious programs can disrupt computer operations, steal sensitive data, and access private networks. Attackers often spread malware through email attachments, infected software downloads, or compromised websites.
Phishing
Phishing attacks are another widespread threat, tricking users into giving away confidential information such as passwords and credit card numbers. Phishers create fake emails and websites that look like they come from reputable sources, leading users to enter personal details, often resulting in financial loss or identity theft.
Ransomware
This severe threat encrypts a user’s files and demands payment for the decryption key. These attacks can paralyze businesses and individuals, and cause significant data and financial loss.
Network Attacks
Network attacks, especially on business networks, can lead to severe breaches. Attackers exploit network vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access, disrupt services, or redirect traffic to malicious sites. Securing network infrastructure requires constant monitoring and updating of security protocols.
Software Vulnerabilities
These are a constant concern since they can be exploited to perform unauthorized actions. Keeping software updated is necessary to defend against exploits targeting these vulnerabilities. Hackers often use these weaknesses to infiltrate systems and spread malware.
Social Engineering
This is a powerful tool for cybercriminals. It exploits human psychology instead of technological flaws to gain access to buildings, systems, or data. Techniques like baiting, pretexting, and scareware manipulate users into making security mistakes.
Insider Threats
Lastly, insider threats, involving employees or contractors who misuse their access to networks, data, or systems, can be particularly hard to detect and prevent. These threats may involve theft of proprietary information or sabotage of computer systems, often discovered only after the damage has occurred.
How to Keep Your Mobile and Computer Secure?
Keeping your mobile devices and computers secure involves using smart strategies and the right tools. Using effective security measures is necessary to protect personal information and sensitive data. Here are the highly recommended ways to do it:
1. Install WOT on Your Browser and Phone
WOT offers a website security extension and app that increases security for both mobile devices and computers. It provides complete protection across all your devices, including these features:
Safe Browsing
It alerts you about risky sites that may have malware or phishing scams before you interact with them. This prevents potential harm.
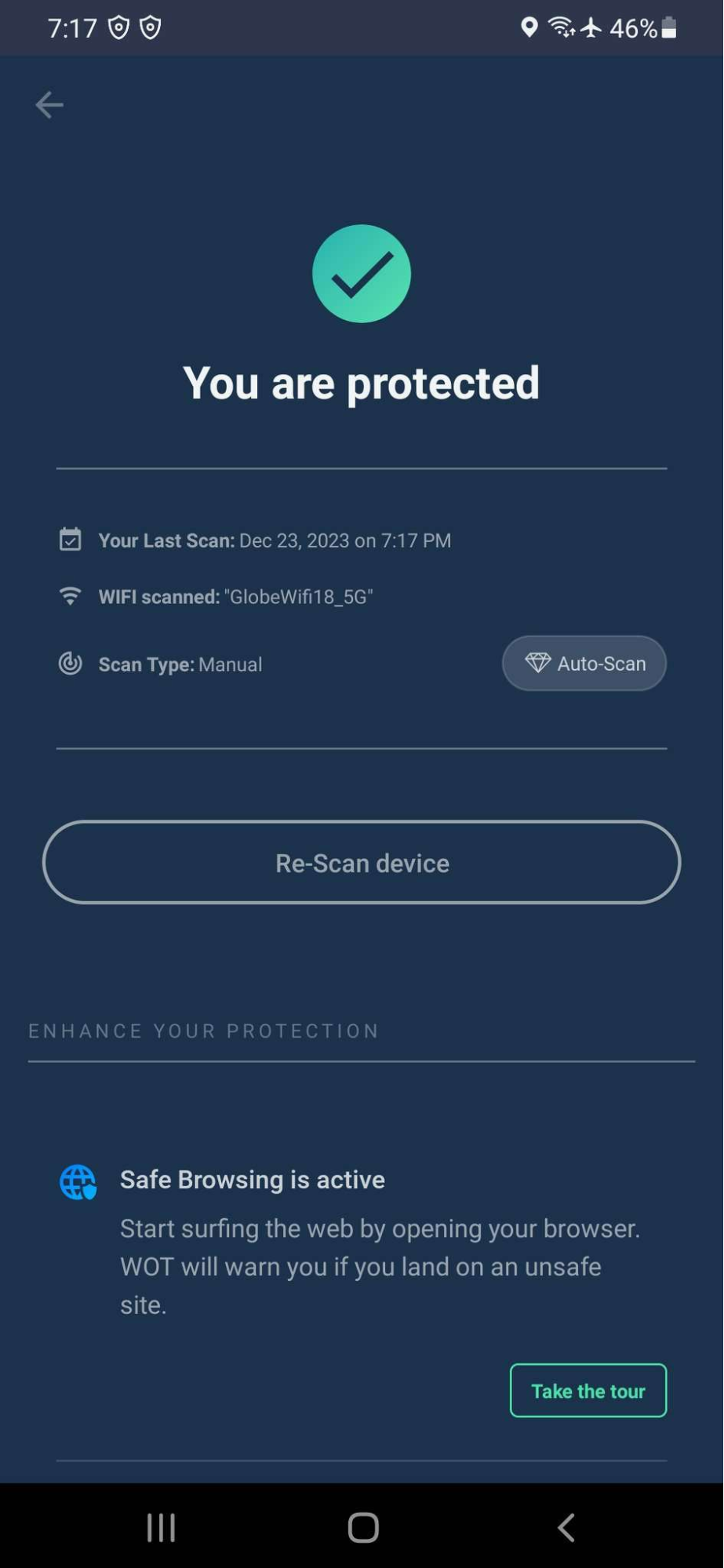
WiFi Scanning
Available only for Android users, WOT’s mobile app scans your network for weaknesses and gives real-time alerts about any unauthorized access or suspicious activities. This helps in improving your network security.
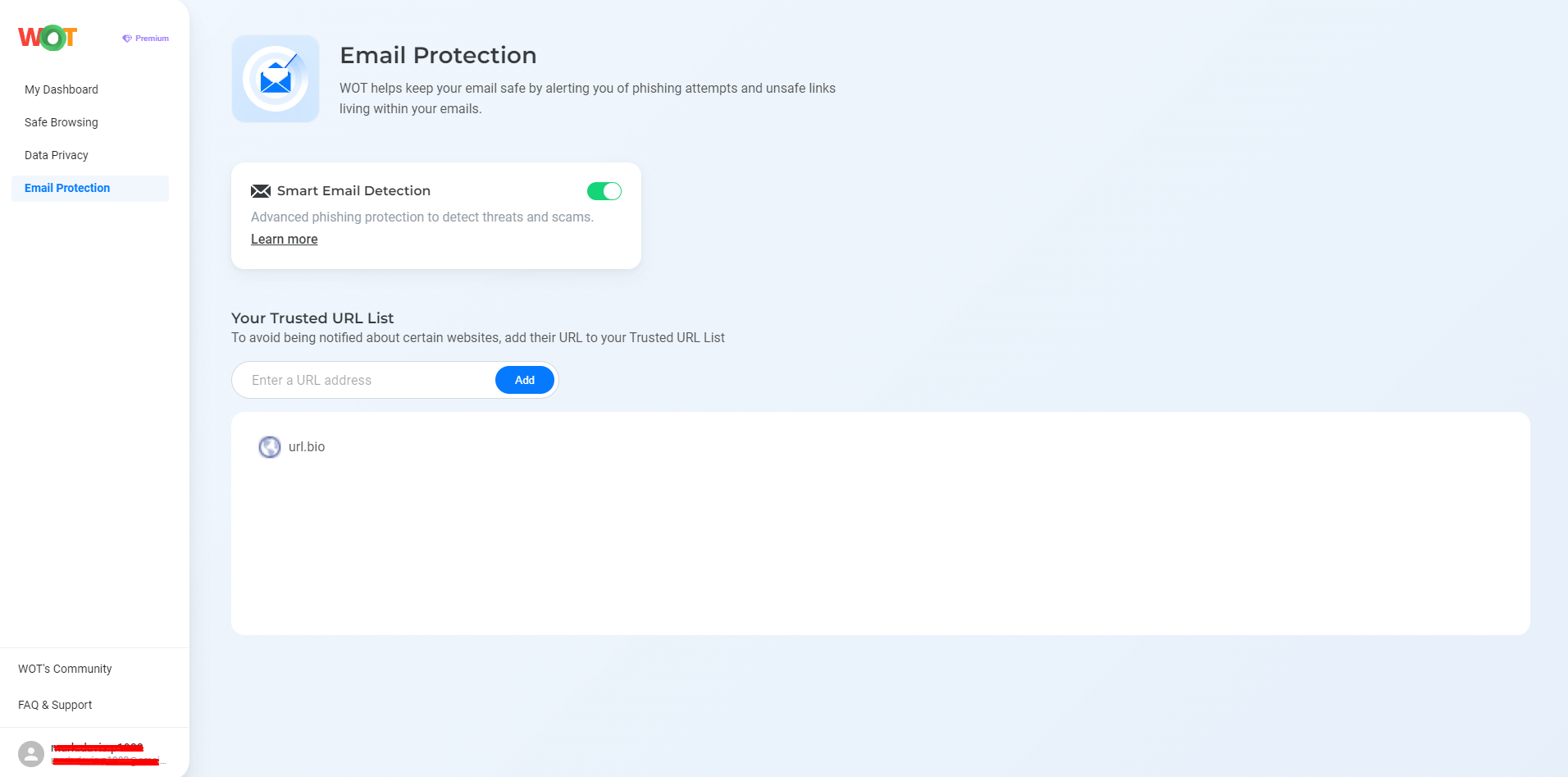
Anti-Phishing
It protects your email by warning you about phishing attempts and unsafe links through its Email Protection feature. Activating Smart Email Detection helps detect threats and suspicious emails, keeping your inbox safe.
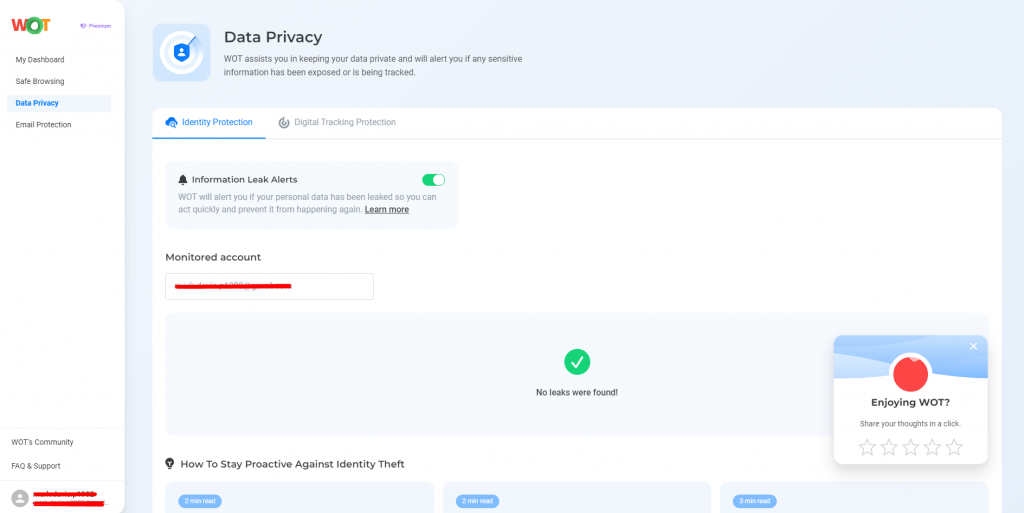
Data Breach Monitoring
WOT keeps your data private by continually checking for any exposure of sensitive information. If your personal data is leaked, it will notify you immediately so you can quickly take action to reduce potential damage.
2. Strong Passwords: Your First Defense Line
Make it a habit of using strong and unique passwords. Each account should have a different password with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Two-Factor Authentication: An Extra Security Layer
Adding an extra layer of security with two-factor authentication greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. This method combines something you know (your password) with something you have (a mobile device or security token), and that makes it much harder for cybercriminals to get in.
4. Secure Wi-Fi Use: Safeguard Your Connection
You need to be aware of the dangers of public WiFi as it can expose your device to many threats. Via these insecure Wi-Fi networks, attackers can intercept your data, so make sure that you don’t use them when making financial transactions or sharing confidential details.
5. Physical Security Measures: Lock and Encrypt
Physical security is often ignored. Always lock your devices when you’re not using them and think about using full-disk encryption to protect your data even in the event that your device gets stolen. Doing this will make all the data on your device unreadable without the correct password or decryption key.
6. Educate Yourself and Others: Knowledge is Power
Staying aware of the latest security threats and learning how to spot them is necessary. You should make use of educational resources and read about safe browsing practices.
7. Anti-Phishing: Stay Clear of Deceptive Sites
Avoid visiting sites that look suspicious or untrustworthy, as they might be trying to steal your personal information. Always check the URL and look for signs of security, like a padlock icon in the browser, to verify that the site is safe.
8. Regular Security Audits: Check and Recheck
Regularly checking your devices for security issues helps you make sure that no new weaknesses are missed. Find tools that can help with these checks and choose one that provides detailed security reports.
10. Regular Updates: Stay Ahead of Threats
Updating your software is necessary to close security gaps that attackers could exploit. Regular updates often include fixes, patches or upgrades for newly discovered vulnerabilities that could compromise your system. Keeping your operating system and applications up-to-date is a simple and effective way to strengthen your defenses.
Security Matters for Both Your Computer and Mobile Devices
Protecting your devices requires a careful plan that combines being alert and using strong security practices. If you know and are aware of the specific dangers that target both mobile devices and computers, you’ll be able to apply customized security steps to protect your personal and work data. Using strong, unique passwords, keeping your software updated, and learning about possible cyber threats are basic steps in creating a safe online space.
Additionally, using trusted security tools like WOT and its features will further strengthen your security position. This keeps both your mobile devices and computers safe from changing cyber threats, helping you maintain privacy and integrity in your online interactions.
FAQs
How often should I update my security software?
You should regularly update to maintain the security integrity of your devices. Software developers frequently release updates to patch vulnerabilities, which hackers exploit. Make the update as soon as patches become available.
What are the most common signs of a security breach?
Indications of a security breach can include unusual account activity, unfamiliar apps installed on your device, sudden changes in your device’s performance, or unexpected pop-ups. It’s important for you to stay vigilant and monitor for these signs so that you’ll be able to quickly take action.
Can a mobile device be as secure as a computer?
Yes, if proper precautions are taken, a mobile device can match a computer’s security level. Precautions include installing trusted security apps, using strong authentication methods, and keeping the operating system updated to defend against any online threats.
What should I do if my device is lost or stolen?
If your device is stolen or lost, try your best to immediately lock it remotely in order to prevent unauthorized access. Most devices come with a feature that will allow you to lock and locate them remotely. After this, notify your service provider and change the passwords for your sensitive accounts as soon as possible.
How can I tell if an app is safe to download?
To verify that an app is safe before downloading, be sure to check if the publisher has good credibility. Check for their user reviews and look for any security certifications. It’s also important that you only download apps from official platforms like the Apple’s App Store or Google’s Play Store, as they conduct preliminary checks to filter out malicious software.
