Every time you log on to a device, it saves heaps of information—from websites visited down to your login details. While this information is quite useful in improving your overall user experience, it can also be quite a privacy risk if several users use the same device. This is where private browsing becomes a necessity. They’re typically designed for short-term use—perfect scenarios being conducting research about a medical condition and not wanting to leave traces behind for other users, or when checking personal email on a public computer.
This browsing method is becoming a common practice these days. Based on a study made by DuckDuckGo, 46.1% of Americans have used private browsing at least once. This feature is offered by various browsers, which differ in certain aspects. Chrome’s Incognito Mode and Firefox’s Private Browsing are some of the more popular ones, with Safari and Edge having similar options as well. These options will help you decide better on enhanced privacy controls over varied situations. We will walk you through everything you need to know about private browsing, its functionalities, and how you could improve your internet privacy practices.
What is private browsing?
Private browsing is an option in almost all of the popular web browsers to browse the internet without saving history, cookies, and form data locally. Chrome calls it Incognito Mode; Firefox and Safari call it Private Browsing. In Edge, it is InPrivate Browsing. This mode especially helps hide browsing history from other people using the same device. However, it’s important for you to be aware that this won’t make you completely invisible on the internet; websites, ISPs, or employers may still follow your activity.
This feature creates a new session in your browser, which works independently of the normal one. You are put in a temporary space where nothing is stored, from cookies to form data. Private browsing fits well in various scenarios, including but not limited to accessing personal accounts without having to log out from other accounts or doing private research on a shared computer. Immediately after the closing of the private window, all such objects, including cached files and cookies, get discarded, proving it effective in all aspects for short-term privacy needs.
While this is indeed a good practice on how to be safe on the internet, most people think that private browsing renders complete anonymity; this again is another misconception. It doesn’t locally store data on your device, but it won’t save your data from network surveillance or tracking so if you want to be safe on public WiFI, then you need to be aware of this. For instance, your online activities can still be logged by your employer or the website you visited. This basic level of privacy is useful for everyday purposes like keeping multiple accounts or situations where data should be treated confidentially.
What does private browsing do?
When the private browsing feature is turned on, it creates a new session, which isolates itself and all its activities from the normal surfing session. Here’s what it does:
Does not save your browsing history
That’s the feature that makes private browsing very useful in many scenarios. The best examples are shopping for a gift privately on a shared computer, managing multiple accounts without interfering with each other’s sessions, and accessing sensitive information without leaving a digital footprint. Moreover, it can be used while on a public computer or network for the purpose of protecting your personal data during a session.
Does not store cookies, site data, or form information
Private browsing mode also stops websites from saving local data, which may be used to customize user experiences and to trace activities on other sites. This feature can prevent your online searches from being curated based on your history because it gives you a more neutral search result. Although private browsing keeps your activity hidden from users of the same device, it doesn’t mask your IP address. This means that other online entities may still be able to monitor your activities.
Disables extensions by default in many browsers unless you manually turn them on
Almost all extensions, especially ad-blockers and password managers, are disabled by default in private browsing. This is to make sure that they do not store any of your data, which would end up leaking your personal information. However, some useful extensions can be enabled manually.
Private browsing vs. anonymous browsing
A lot of people are generally confused between private browsing and anonymous browsing. Private browsing simply conceals your activities from other users of a specific device but in no way anonymizes your persona on the internet. For example, take your IP address; it is traceable, and the websites will still be able to identify you using different tactics. In contrast, anonymous browsing provides a much greater level of privacy, which is attained through the use of technologies such as VPNs and Tor. These services mask your IP address while encrypting data, so no service provider or website can easily trace what you are up to.
While private browsing offers convenience and a basic level of privacy, its privacy capability cannot be compared to that of anonymous browsing. For example, VPNs not only work to mask your IP address but also provide added security measures through data encryption. A Tor browser works by routing your Internet traffic across nodes, making it hard to track down activities. Coupling private browsing with other privacy tools will build a stronger defense against online tracking and keep your activities private under varied circumstances.
Private browsing helps in tasks that require confidentiality but need not be fully anonymous. Situations include casual activities like logging into multiple accounts or personal searches. However, greater degrees of anonymity online are required by certain activities, and more tools should be used in order to achieve them. These tools reroute your internet traffic so it’s really hard to track activities comprehensively.
Knowing the difference between private browsing and anonymous browsing will help you in making better decisions for online privacy. As private browsing provides momentary privacy to people, anonymous browsing protects against all those varied ways of tracking. Integrating them provides a safe browsing experience that covers all bases of online privacy.
Reasons for using private browsing
Understanding the reasons opens up several other use cases that remain valid enough to use private browsing. This can help you effectively use this feature for the right purposes:
Shopping for presents
This is one of the top reasons to use private browsing. It helps in keeping secret the gift ideas or surprise plans on shared devices such that no one bumps into your searches unknowingly.
Multi-account management
It eases the management of multiple logins without any conflicts in sessions. For example, you can check your emails on a personal account while remaining logged in to a work account in another tab, without any sort of interference.
Accessing sensitive information
Private browsing can make your medical or legal research confidential from others who are using the same device. This is a very useful feature when researching from shared or public places.
Unbiased results
This will help in running searches that are not biased from the results that were provided in earlier searches. More unbiased search results, not influenced by your surfing habits performed earlier, are extremely useful in professional research and price comparisons.
Private browsing on public computers
This is where private browsing ensures that the personal data doesn’t hang around on a machine once you log off. It prevents subsequent users from accessing any of your session data and keeps your information safe.
What is a private browser?
A private browser is a browser that offers the opportunity to surf the net without recording any session data. Private or incognito modes are available on practically all the most recent browsers to prevent history, cached files, and cookies from being saved when they are turned on. Some of the browsers that have such functions are:
- Chrome
- Firefox
- Safari
- Edge
- Opera
The basic level of privacy might be handy in some cases, but it doesn’t feature full anonymity. You’ll need to further keep your privacy secure by using tools like VPNs or some privacy-focused browser extensions.
For example, Chrome’s Incognito Mode works just for your current session but your activity is still visible to your ISP. Firefox’s Private Browsing also comes with in-built tracking protection that blocks known trackers, which adds a shield against surveillance. In this mode, Safari blocks websites from tracking your search behavior and can give you a clean slate. For Microsoft Edge, there’s InPrivate Browsing, which pretty much does the same thing, just like the private mode in Opera, with added ad blocking.
With the advancement in technology, private web browsers are getting very popular and in high demand. Awareness about privacy continues to grow, and it has increased the demand for features that can prevent data from being tracked and stored. Safari has since been praised for its strict privacy stance, allowing private browsing with more aggressive blocking against advertiser tracking. The innate features of this browser enable users to safely browse the internet without the prying eyes of data collectors.
Microsoft Edge, previously known as Internet Explorer, has also revamped its image with the use of many enhanced privacy features through its InPrivate Browsing mode. This allows secure browsing sessions and keeps users’ data private from trackers. This change typifies the need to develop strong personal privacy protocols within majorly used web browsers to retain trust and faith amongst the users. It is not only the individual user Edge’s InPrivate browsing aims to serve but also enterprises that require controlled and secure browsing environments.
Opera is often undermined by its peers. It has a private browsing mode, coupled with an effective built-in VPN. This in itself makes it quite a powerful combination for security purposes, assuring users of more reliable provisions of privacy mechanisms. Usability and features are important reasons to pick the right privacy-oriented browser. An excellent web browser for privacy does not really grant privacy, but gives peace of mind; you feel rest assured that your activities are not being sniffed somewhere or logged.
How to use private browsing on your browser
It is easy to turn on private browsing with most browsers. Each has made it quite easy to enter private mode and thus easily accessible to their users. Below are the simple-to-follow steps to turn on private browsing among different browsers:
Chrome
For desktop
Click on the three dots at the top-right corner and select “New Incognito Window,” or press Ctrl+Shift+N, or Cmd+Shift+N.
For mobile
Open Chrome, click on the icon with three dots, and select “New Incognito Tab.”
Safari
For desktop
Enter File Menu and then select “New Private Window” or press Shift+Cmd+N.
For Mobile
Tap the Tabs button, swipe to the Private tab button on iOS 17 or higher. Swipe to the Private tab button on iOS 16 and earlier.
Firefox
For desktop
Click the three lines then “New Private Window” or use Ctrl+Shift+P (Cmd+Shift+P on Mac).
For mobile
Tap on the tab icon, click on the mask button, and tap on the plus sign to start browsing privately.
Edge
For desktop
Click the three dots and select “New InPrivate window” or press Ctrl+Shift+P (Cmd+Shift+P on Mac).
For mobile
Tap the three dots and select “New InPrivate tab.”
Opera
For desktop
Click the Opera logo and then select “New private window”, or use Ctrl+Shift+N (Cmd+Shift+N on Mac).
For mobile
Tap the Tabs icon followed by Private.
Stay safe when browsing privately with WOT
While private browsing provides some amount of privacy because no data gets stored locally in the session, such protection is relatively very limited. Web of Trust (WOT) can improve your private browsing experience by keeping you safe from various dangers.
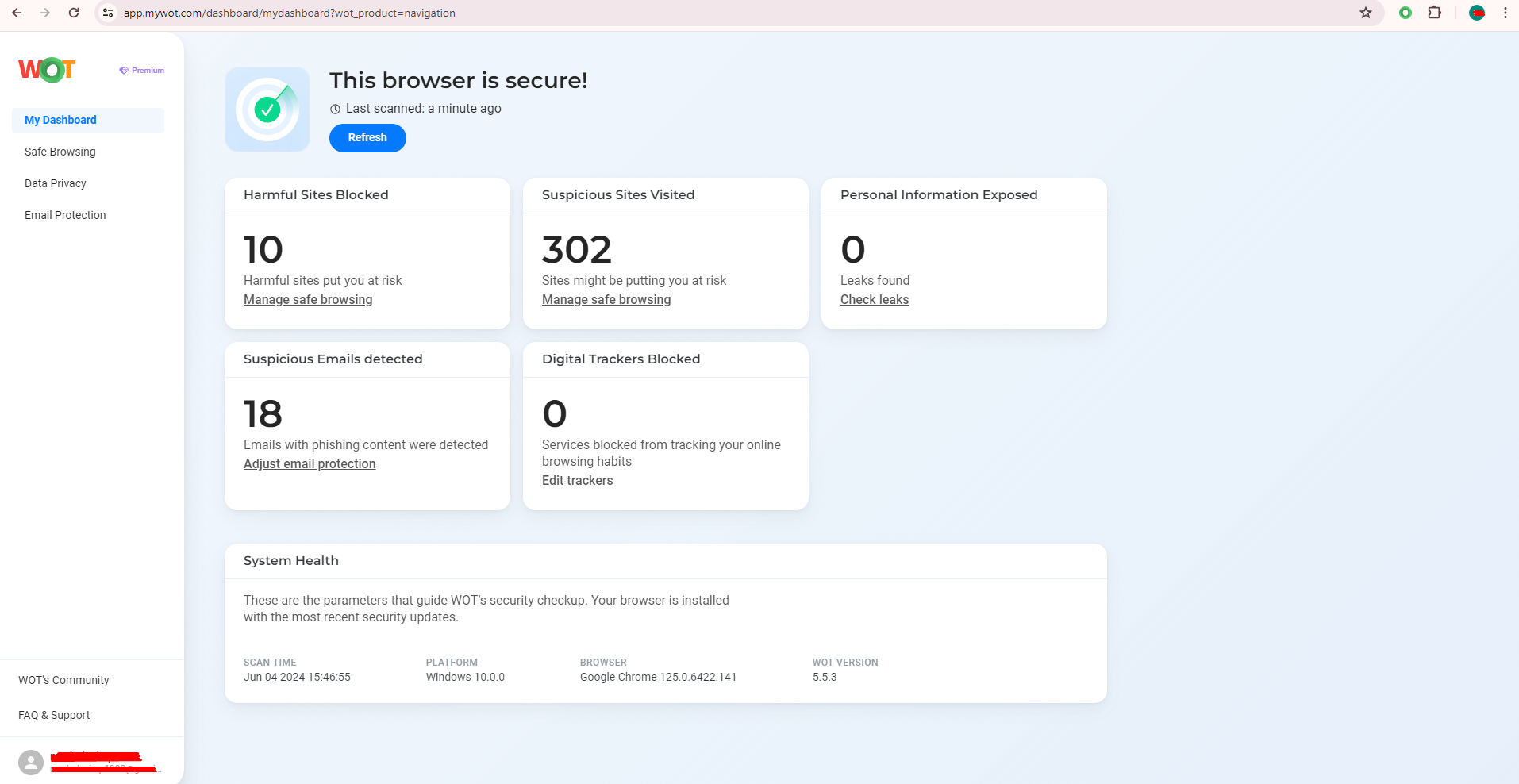
WOT extends private browsing with its Safe Browsing feature, where it checks on your online interactions and warns against visiting malicious websites. As the percentage of online threats increases, it’s wise to combine WOT with your browsing for significant security advantages. In this regard, it is recommended to have WOT together with private browsing modes for more protection online. The tool gives real-time warnings before one is exposed to a harmful website, thus keeping you protected at all times.
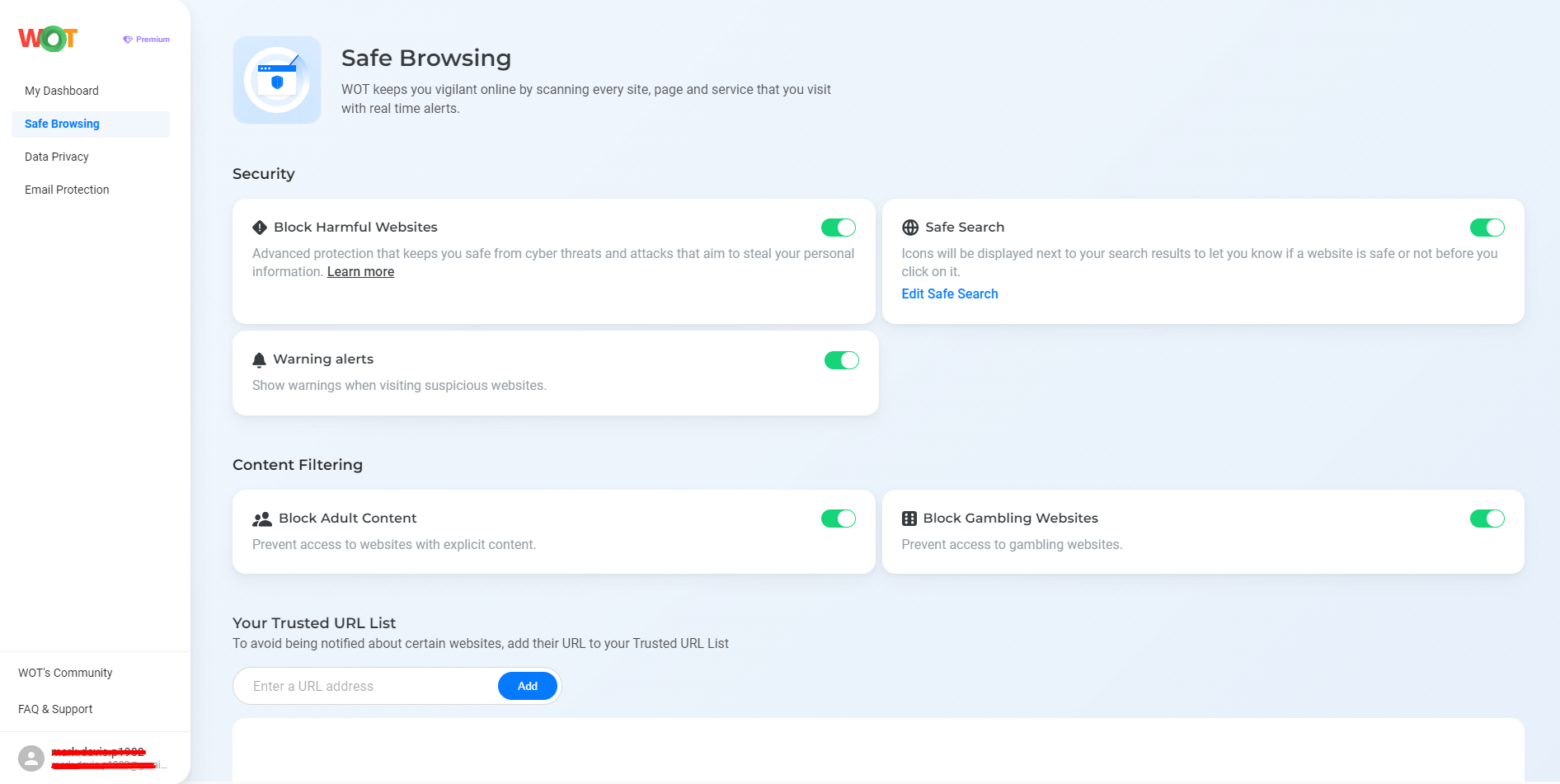
WOT is easily installed and integrates with most browsers to extend the scope of protection beyond what private browsing can do. Another very important protective feature is anti-phishing, which warns users against malicious links and sites. This forms a very important layer of defense that private browsing alone cannot offer. This feature is quite indispensable for all who are concerned about cyber threats and data breaches since phishing scams remain to be one of the primary methods cybercriminals apply in stealing sensitive information.
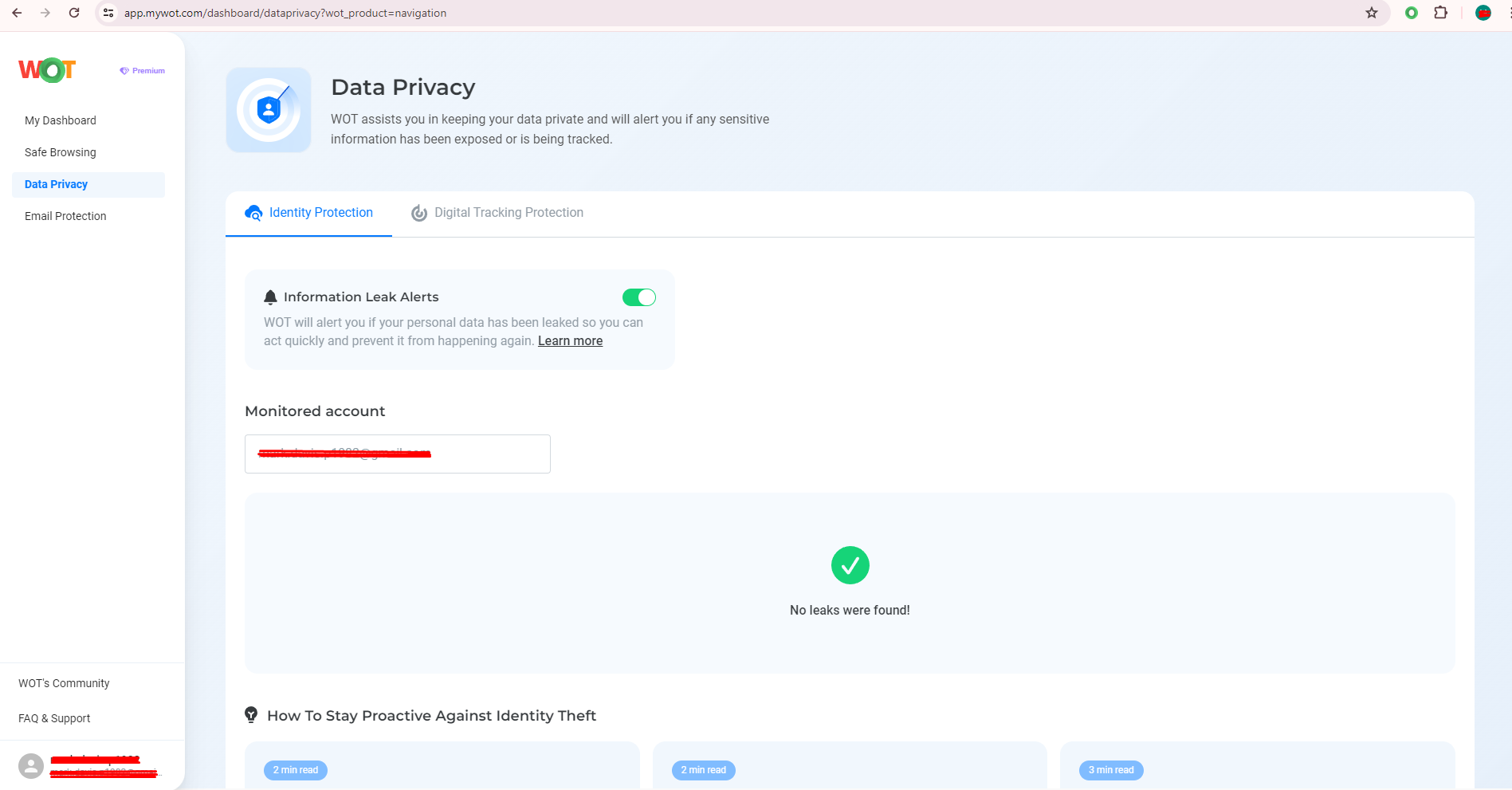
Content filtering on Android is targeted at giving users a secure window for safe browsing. Its premium version blocks inappropriate or unsafe content and thereby makes web use much more secure, especially for children. It keeps the online environment cleaner and more secure by actively filtering unwanted content. Its URL list functionality keeps the user in control and in a position to enjoy a customized browsing experience with unwanted sites closed to one’s view. This free version supports up to three URLs; the unlimited version is available with browser extensions, providing the required flexibility for personalized protection.
The final step for enhanced privacy
Coupled with WOT’s comprehensive suite for security, private browsing can very well become a game-changer for your overall online safety. This peace of mind comes from knowing that not only is your local data hidden, but real-time protection for your browsing sessions is provided.
Run private browsing mode and take maximum advantage of WOT to have a secure online experience. Don’t be caught off guard; take control of privacy and data now.
FAQs
Will private browsing stop all tracking?
Private browsing prevents your history and cookies from being locally stored but does not prevent websites, ISPs, or network administrators from tracking what you visit or what you are doing.
Is private browsing available on all devices?
Yes. All popular browsers implement private browsing on all devices, from desktops and laptops to tablets and smartphones.
What are the limitations of private browsing?
Private browsing does not provide total anonymity. Activities can still be attributed to you through network-level surveillance, malware, and some forms of tracking.
Can I use extensions in private browsing mode?
This is browser-dependent. Some browsers will allow extensions to run in private mode, but generally, most extensions are turned off in a private browser to avoid leakage of information. Go to the browser settings to turn them on or to configure them.
How do I configure my browser for increased privacy beyond private browsing?
You can further improve your privacy with the use of tools like VPNs and privacy-oriented browser extensions, which aid in encryption and try to minimize the attempt to track your actions by different parties.
